CHAPTER 9
810
Multimedia Features
far planes, respectively. A value of
ANF
for
CS
means that the near and far planes
are determined automatically based on the objects in the artwork.
The
Subtype
entry specifies the type of projection, which determines how objects
are projected onto the near plane and scaled. The possible values are
O
for
ortho-
graphic projection
and
P
for
perspective projection.
For orthographic projection, objects are projected onto the near plane by simply
discarding their
z
value. They are scaled from units of the near plane’s coordinate
system to those of the annotation’s target coordinate system by the combined fac-
tors specified by the
OS
entry and the
OB
entry.
For perspective projection, a given coordinate (x,
y, z)
is projected onto the near
plane, defining a 2D coordinate (x
1
,
y
1
) using the following formulas:
n
-
x
1
=
x
×
--
z
n
-
y
1
=
y
×
--
z
where
n
is the
z
coordinate of the near plane.
Scaling with perspective projection is more complicated than for orthographic
projection. The
FOV
entry specifies an angle that defines a cone centered along
the
z
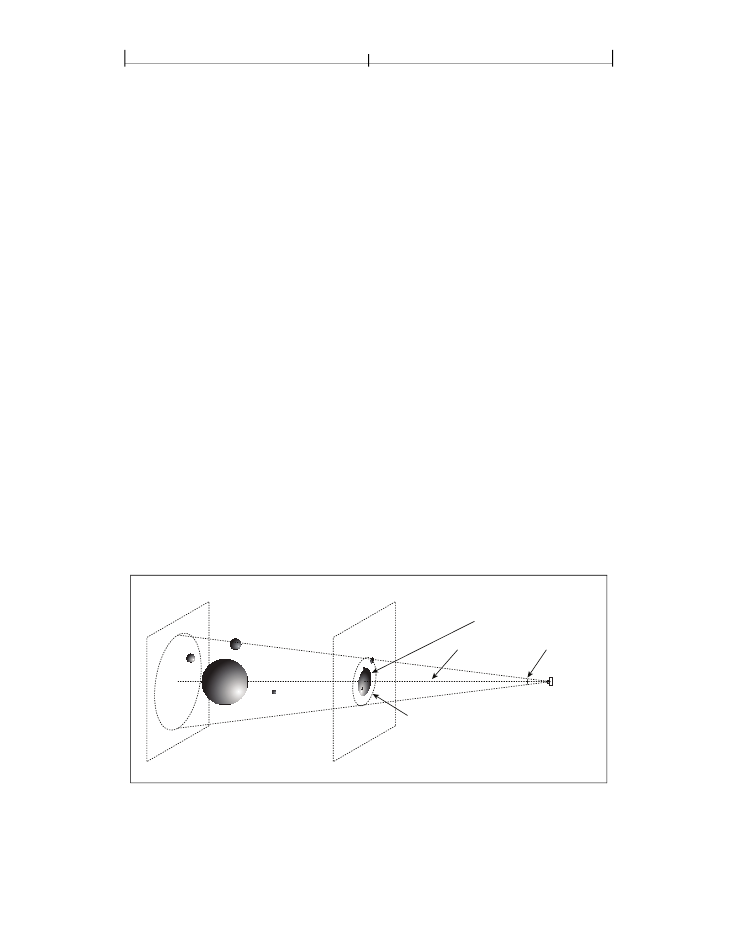
axis in the camera coordinate system (see Figure 9.5). The cone intersects
with the near plane, forming a circular area on the near plane. Figure 9.6 shows
this circle and graphics from the position of the camera.
Far Clipping Plane
Near Clipping plane
Objects projected onto near clipping plane
Z axis
Field of View angle
Circle defined by Field of View angle on near clipping plane
FIGURE 9.5
Perspective projection of 3D artwork onto the near plane