SECTION 4.6
325
Patterns
ta.
As in free-form triangle meshes (type 4), each patch has an
edge flag
that indi-
cates which edge, if any, it shares with the previous patch. An edge flag of 0 begins
a new patch, unconnected to any other. This must be followed by 12 pairs of co-
ordinates,
x
1
y
1
x
2
y
2
…
x
12
y
12
, which specify the Bézier control points that
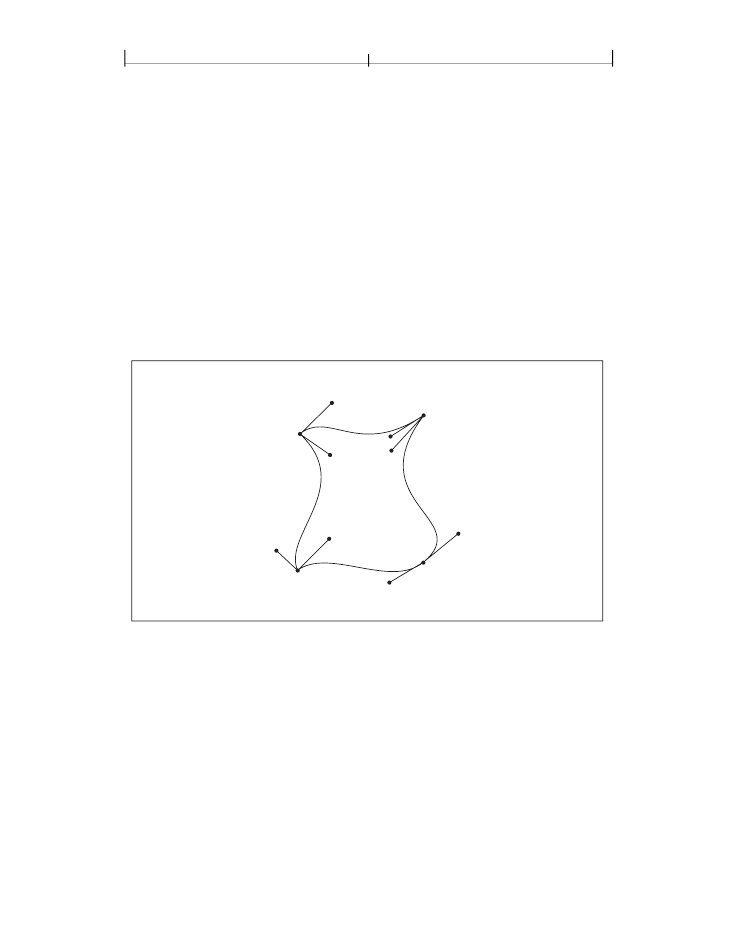
define the four boundary curves. Figure 4.22 shows how these control points cor-
respond to the cubic Bézier curves
C
1
,
C
2
,
D
1
, and
D
2
identified in Figure 4.20 on
der as the control points corresponding to the corners. Thus,
c
1
is the color at co-
ordinates (x
1
,
y
1
),
c
2
at (x
4
,
y
4
),
c
3
at (x
7
,
y
7
), and
c
4
at (x
10
,
y
10
), as shown in the
figure.
Use this side when next
f
= 1.
5
c
2
C
2
4
3
This side already attached
to previous patch. Start a
new patch when next
f
= 0.
D
1
6
8
D
2
Use this side when next
f
= 2.
7
c
3
12
2
1
c
1
C
1
11
10
c
4
9
Use this side when next
f
= 3.
FIGURE 4.22
Color values and edge flags in Coons patch meshes
=
1, 2, or 3) connect
a new patch to one of the edges of the previous patch. In this case, some of the
previous patch’s control points serve implicitly as control points for the new patch
as well (see Figure 4.23), and therefore are not explicitly repeated in the data
stream. Table 4.35 summarizes the required data values for various values of the
edge flag.