TIFF 6.0 Specification
Final—June 3, 1992
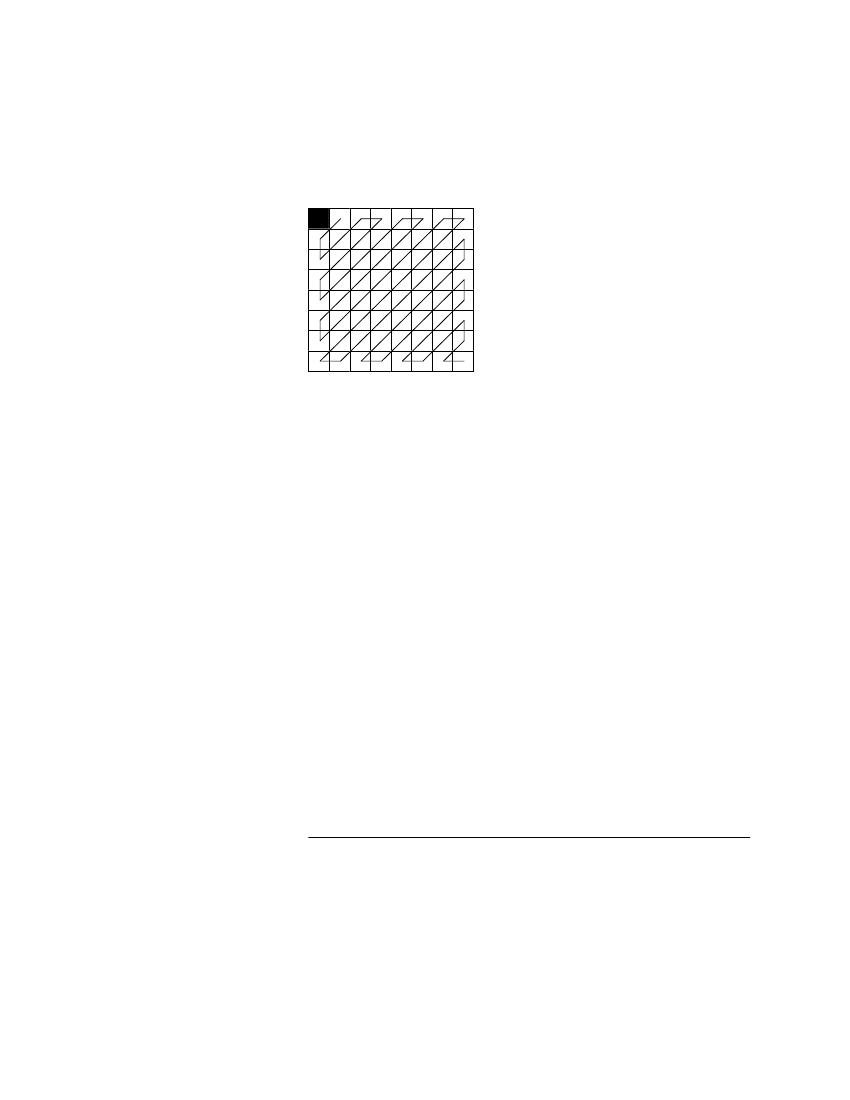
Zig-Zag Scan
Prior to entropy coding, the DCT coefficients are ordered into a one-dimensional
sequence according to a “zig-zag” scan. The DC coefficient is coded first, fol-
lowed by AC coefficient coding, proceeding in the order illustrated in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Zig-Zag Scan of DCT Coefficients
Entropy Coding
The quantized DCT coefficients are further compressed using entropy coding.
The baseline process performs entropy coding using variable length codes (VLCs)
and variable length integers (VLIs).
VLCs, commonly known as Huffman codes, compress data symbols by creating
shorter codes to represent frequently-occurring symbols and longer codes for
occasionally-occurring symbols. One reason for using VLCs is that they are easily
implemented by means of lookup tables.
Separate code tables are provided for the coding of DC and AC coefficients. The
following paragraphs describe the respective coding methods used for coding DC
and AC coefficients.
DC Coefficient Coding
DC prediction produces a “differential DC coefficient” that is typically small in
magnitude due to the high correlation of neighboring DC coefficients. Each dif-
ferential DC coefficient is encoded by a VLC which represents the number of
significant bits in the DC term followed by a VLI representing the value itself.
The VLC is coded by first determining the number of significant bits, SSSS, in the
differential DC coefficient through the following table:
SSSS
0
1
2
3
4
5
Differential DC Value
0
-1, 1
-3,-2, 2,3
-7..-4, 4..7
-15..-8, 8..15
-31..-16, 16..31
98